What is a Domain Name?
When you type in a web address, you are typing in the URL or Uniform Resource Locator. It is basically your address on the internet, and it is what any user will need to find your site. We will study the structure of the internet throughout this course.
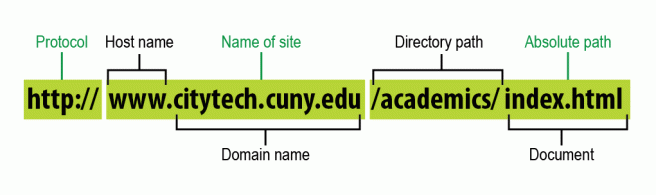
A full URL from this site is made up of three components: the protocol, the site name and the absolute path to the document or resource.
The Parts of a URL
- Protocol
- Name of Site
- Absolute path
- http: the protocol, or type of server your web browser is talking to
- www: The URL hostname, in this case, the world wide web
- citytech.cuny.edu: the specific domain name, and the part you register. If you did not have a domain name, you would have to remember the specific IP address (Internet Protocol address) for your site location on a server somewhere. An IP address is a series of numbers, such as 192.168.9.100. Hard to remember for us non-robotic types.
- com: top-level domain: this is another way to distinguish sites. You have noticed other sites ending in .net, .gov… the top domain indicates something of what the site’s general purpose.
- academics: directory path
- index.html: document